Septic Arthritis Vs Osteomyelitis: Septic arthritis is an infection in a joint; osteomyelitis is an infection in bone. Both conditions require prompt medical attention to avoid serious complications.
Understanding the differences between septic arthritis and osteomyelitis is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. These conditions, though related by their infectious etiologies, affect different structures within the skeletal system. Septic arthritis targets the joints, including the synovial fluid and joint lining, presenting with symptoms like joint swelling, warmth, and pain that can hinder movement.
Osteomyelitis, however, is characterized by the infection of bone tissue potentially including the marrow, leading to symptoms such as localized pain and possibly fever. Despite the distinct areas of prevalence, both conditions can cause significant discomfort and are often associated with similar causative agents, like Staphylococcus aureus. Quick detection and medical intervention are keys to managing these infections and mitigating potential long-term damage to the skeletal system.
Introduction To Bone And Joint Infections
Bone and joint infections are serious medical conditions. Osteomyelitis refers to an infection in the bone, while septic arthritis involves infection in a joint. They are different, yet both require quick medical attention.
Telltale Signs Of Bone Infections
Bone infections such as osteomyelitis can be hard to spot. Watch for these signs:
- Sudden, severe pain in a bone
- Fever and chills that come on quickly
- Redness or warmth over the affected area
- Swelling that makes the skin tight
Common Symptoms Of Joint Infections
Septic arthritis often shows itself through symptoms like:
- Joint swelling and pain that gets worse with movement
- Fever that may seem mild at first
- Warmth and redness around the joint
- Limited range of motion in the joint
Demystifying Septic Arthritis
Introduction to Demystifying Septic Arthritis
Understanding Septic Arthritis starts with breaking down myths and knowing the facts. It’s a joint infection, not just regular joint pain. It can attack any joint, but it loves knees the most. Quick action can mean the difference between a speedy recovery and long-term problems. Let’s dig into the causes and symptoms of Septic Arthritis.
Pathophysiology of Septic Arthritis
Pathophysiology Of Septic Arthritis
- Bacteria or viruses invade the joint space.
- The immune system reacts, causing inflammation.
- Toxins from the pathogens damage the cartilage.
- The synovial fluid increases, leading to swelling and pain.
Septic Arthritis is a direct attack on your joints leading to redness, pain, and can limit movement if not treated early.
Presentation of Septic Arthritis
Presentation Of Septic Arthritis
Know these signs:
- Sudden severe joint pain that worsens with movement.
- Swelling and redness over the joint.
- It might bring fever, chills, and feel warm to the touch.
Each symptom is a cry for help. They signal it’s time to see a doctor.
Diagnostic Process of Septic Arthritis
Diagnostic Process Of Septic Arthritis
Diagnosing starts with listening to your body and talking to your doctor. Here is what comes next:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Doctor checks your symptoms. |
| 2 | Blood tests search for infection-fighting cells. |
| 3 | Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs show joint damage. |
| 4 | Synovial fluid analysis checks the fluid for bacteria. |
Treatment begins soon after a confirmed diagnosis to protect your joints and your health.
Understanding Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection. It occurs when bacteria or fungi invade a bone. These germs can reach a bone through your bloodstream. They can also spread from nearby tissue, or due to an injury. Children and adults can both get osteomyelitis. But it requires quick attention to prevent serious complications.
Bone Involvement And Symptoms
Osteomyelitis can affect any bone in the body. The symptoms can vary. Common signs include:
- Pain in the affected bone
- Fever and chills
- Swelling, redness, and warmth in the area
The severity of these symptoms can range from mild to severe. It depends on the disease progression.
Diagnosing Osteomyelitis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose osteomyelitis. They look at your medical history and symptoms. They also order tests like:
| Test Type | What It Helps Determine |
|---|---|
| Blood Tests | Signs of infection and inflammation |
| Imaging | Exact location and damage to bone |
| Bone Biopsy | Type of germ causing the infection |
A bone biopsy is the surest way to diagnose. Doctors take a small sample of the affected bone to test. The results help in creating the best treatment plan.
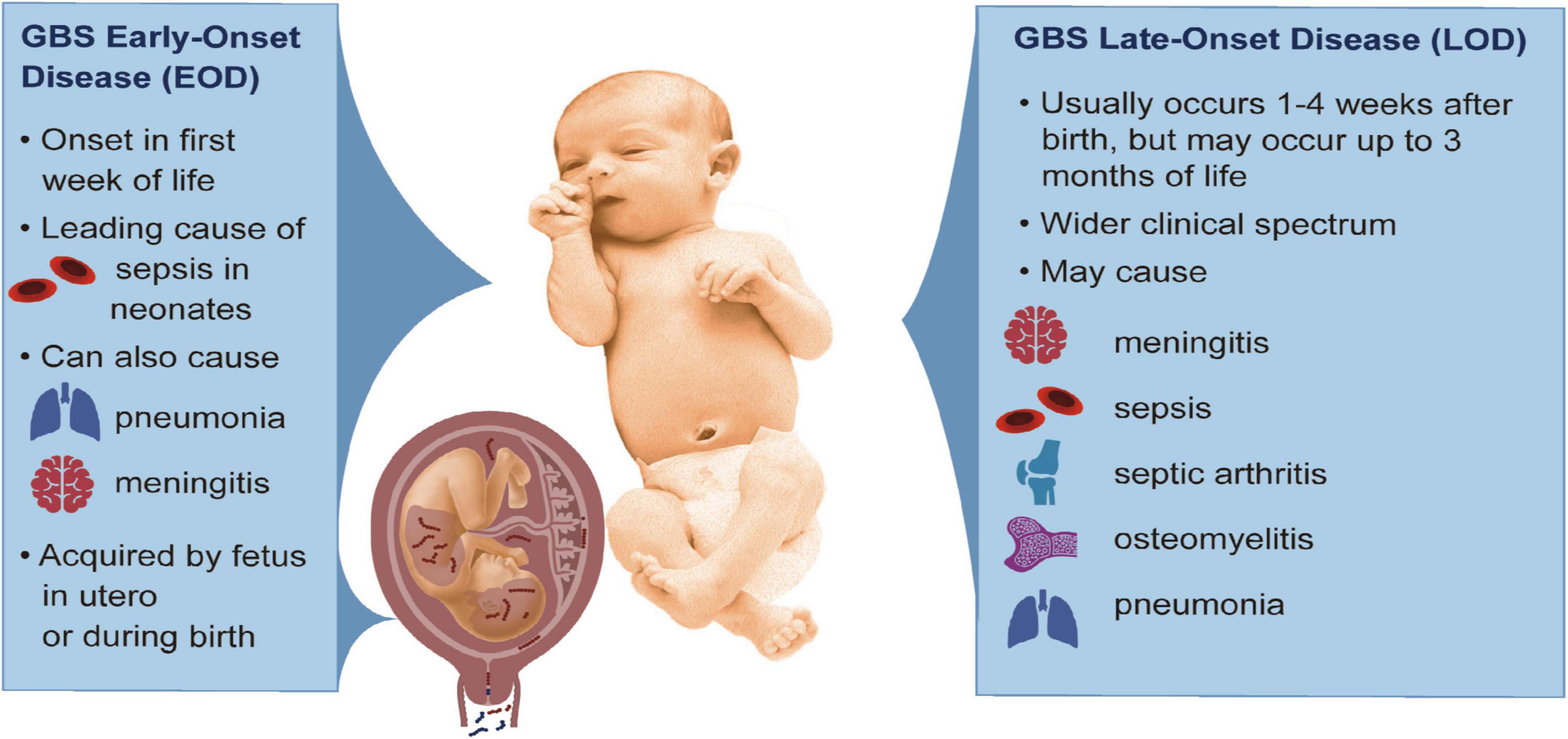
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
Comparative Pathogenesis
Exploring the root causes of Septic Arthritis and Osteomyelitis reveals a sinister world of bacterial onslaughts against our musculoskeletal fortress. These conditions share connections but hold distinct battlefields where bacteria wreak havoc in different ways.
Bacterial Agents: Common And Different
Septic Arthritis and Osteomyelitis often host unwelcome guests, but not always the same types. Staphylococcus aureus stars as the common culprit, while others play roles based on the infection’s address in the body.
- Staphylococcus aureus: Both conditions’ main antagonist.
- Streptococci: More frequent in Septic Arthritis.
- Gram-negative bacilli: Can be unique to Osteomyelitis.
Infection Sites And Systemic Impact
Microbes in Septic Arthritis prefer joints, while those in Osteomyelitis invade bone. The infection sites shape their systemic story differently.
| Condition | Infection Site | Systemic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Septic Arthritis | Joints (synovial fluid and lining) | Acute inflammation, potential joint damage |
| Osteomyelitis | Bone (marrow and cortex) | Chronic bone destruction, possible bloodstream invasion |
Treatment Strategies And Challenges
Both septic arthritis and osteomyelitis require prompt and effective treatment. These conditions can be complex to manage. The goal is to eradicate the infection quickly to prevent joint destruction or bone damage. Careful consideration of antibiotic therapy and the timing of surgery are critical.
Antibiotic Therapy Nuances
Selecting the right antibiotic is key in treating both conditions. Culture results guide the choice of antibiotics. Sometimes, this requires a broad-spectrum approach, later narrowing down based on culture sensitivities.
- Length of therapy varies from weeks to months.
- Intravenous antibiotics may transition to oral forms.
- Monitoring for antibiotic resistance is necessary.
When Surgery Comes Into Play
Surgery might be needed when infections are severe. It helps remove infected tissue and drain pus. This is vital to ensure the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy.
- Arthroscopic surgery: for septic arthritis to clean the joint.
- Open surgery or debridement: to remove infected bone in osteomyelitis.
- Reconstructive surgery: may follow to restore function.
The decision to operate depends on the infection’s location and severity, and the patient’s response to antibiotics.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Preventing Complications And Recurrence
Both Septic Arthritis and Osteomyelitis demand swift medical attention due to potential severe complications. Preventing complications and recurrence is critical for long-term health. Key factors include early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and vigilant follow-up care.
The Role Of Early Intervention
Early intervention plays a pivotal role in managing these infections. It stops the infection from causing further damage.
- Seek immediate medical help if symptoms appear.
- A correct diagnosis prevents the spread of the infection.
- Start antibiotics and other treatments as soon as possible.
Long-term Care And Monitoring
After the initial treatment, long-term care ensures recovery and helps avoid future issues.
- Regular doctor visits to monitor recovery.
- Tests to ensure the infection is fully resolved.
- Physical therapy may be necessary for rehabilitation.
Patients must be proactive and maintain contact with their healthcare providers. Inform your doctor of any new symptoms.

Credit: www.mdpi.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Septic Arthritis Vs Osteomyelitis
How Do You Rule Out Septic Arthritis?
To rule out septic arthritis, doctors perform arthrocentesis for synovial fluid analysis and order blood cultures and imaging studies.
When Should You Suspect Septic Arthritis?
Suspect septic arthritis with sudden, severe joint pain, swelling, redness, and fever.
What Are The Three Stages Of Septic Arthritis?
The three stages of septic arthritis are acute, subacute, and chronic.
What Are The Diagnostic Criteria For Septic Arthritis?
Diagnostic criteria for septic arthritis include joint pain, swelling, warmth, erythema, and limited movement. Fever and lab tests support diagnosis; definitive confirmation requires synovial fluid analysis.
What Are Symptoms Of Septic Arthritis?
Septic arthritis typically presents with severe joint pain, swelling, redness, and decreased range of motion. Fever and chills may also accompany these symptoms.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances distinguishes septic arthritis from osteomyelitis is critical for anyone facing joint pain and infection concerns. Both conditions demand prompt medical attention to prevent serious complications. As we’ve explored their differences, symptoms, and treatment options, remember that early detection is key.
Empower yourself with knowledge and seek timely care for joint health and well-being. Keep this guide in mind should you ever need to distinguish between these two serious infections.

